In Maropost Commerce Cloud, products are managed through a structured Product Details page. This page combines all core catalog entities into an intuitive layout, allowing merchants to manage product information, availability, pricing, SEO, and custom data from one place.
Below is an overview of each section, aligned with the actual UI sequence in Commerce Cloud.
1. General Information
This section contains the core identification and descriptive details for your product. It defines what the product is, how it is titled, and the basic content customers will see.
You can add a subtitle for a tagline, toggle whether the product can be discounted, and choose the sales channels it will be available in — for example, your online store, a POS location, or a marketplace integration.
Fields include:
- Title – The product name shown in the storefront.
- SKU – Unique identifier for the default variant (if no variants are created).
- Subtitle – Optional secondary title or tagline.
- Description – Rich text editor for product details, features, and marketing copy.
- Product Status – Published (visible in the storefront) or Unpublished (hidden).
- Sales Channels – Select where the product is sold (Online Store, POS, Marketplaces).
- Discountable toggle – Determines whether discounts can be applied.
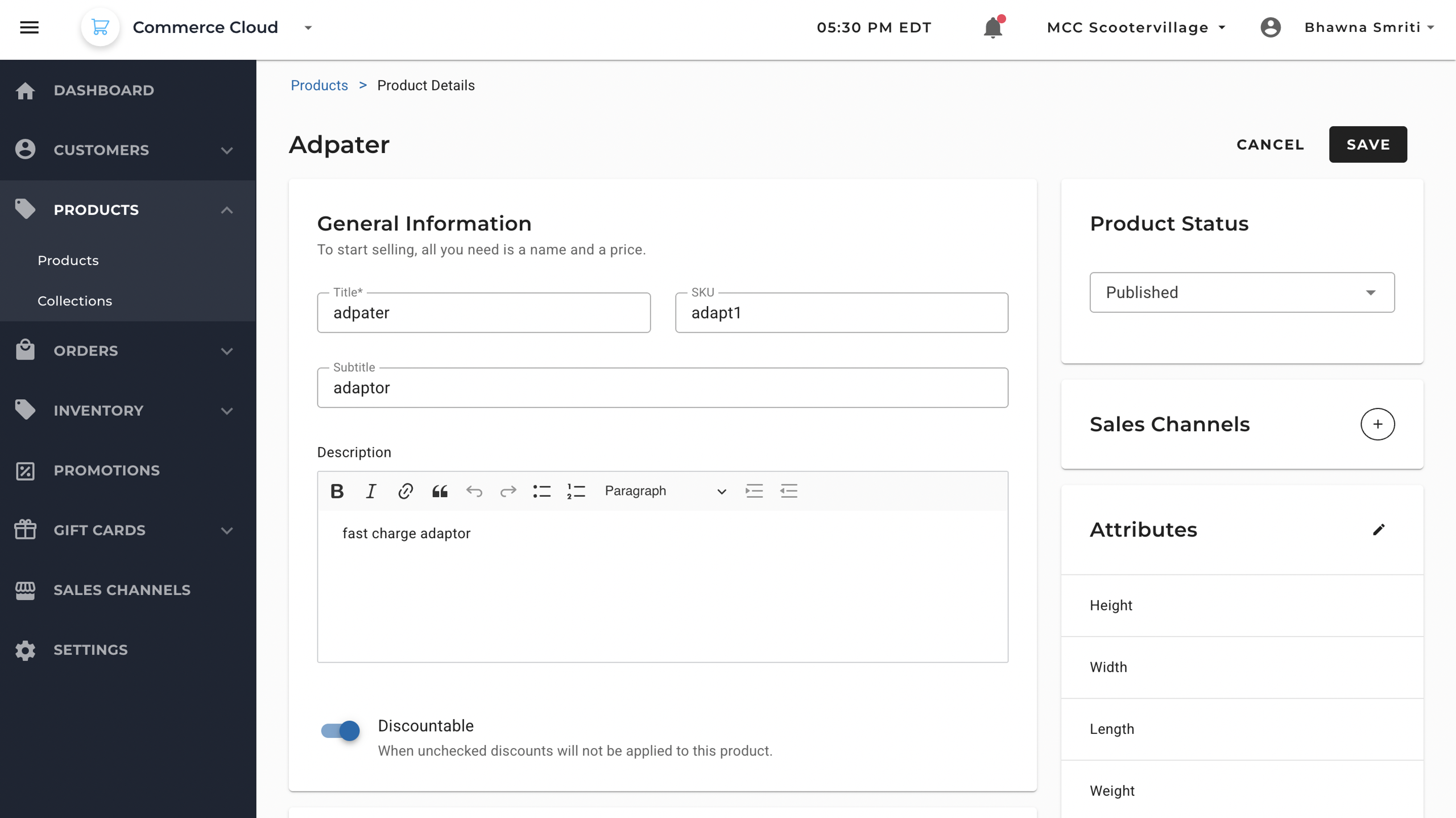
If you sell different versions of a product (such as multiple sizes or colors), you can decide whether to treat it as a single product or enable variants. If “Yes, this is a product with variants” is enabled, the product will support multiple variant configurations using attributes like size, color, or material.
In case of multiple variant option, the system will automatically create each variation, based on the details provided.
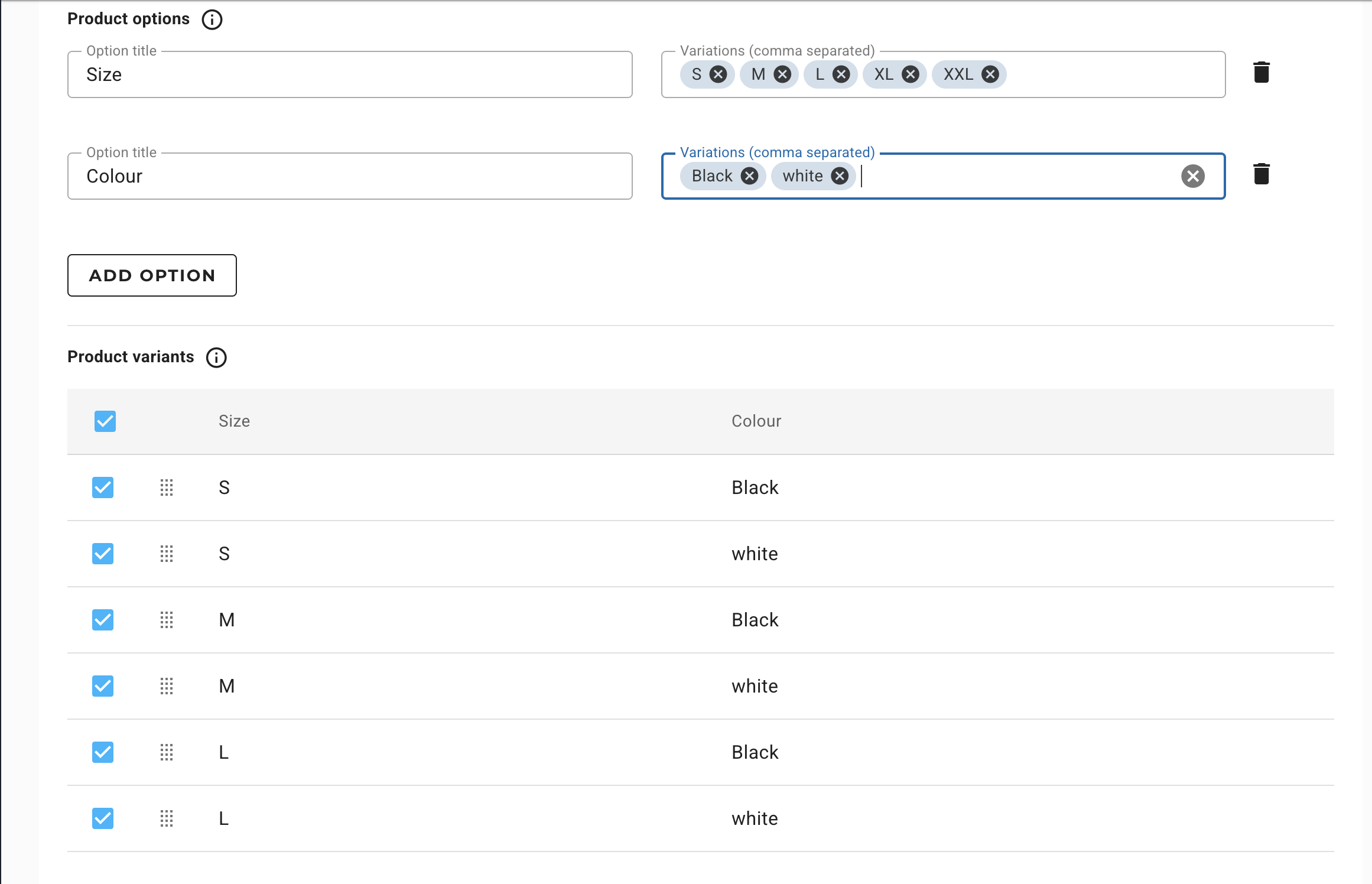
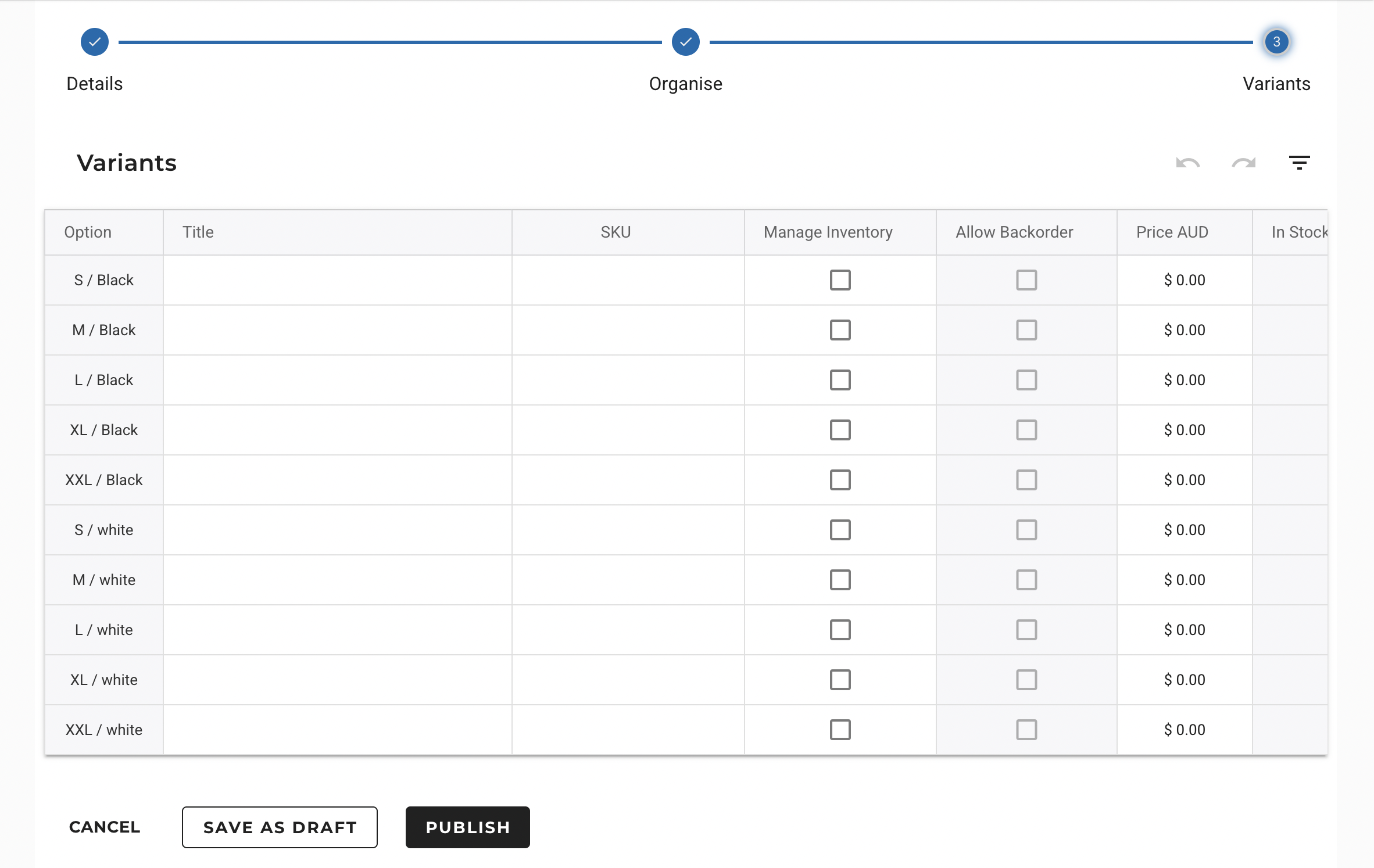
2. Attributes
Attributes define the product characteristics that differentiate variants. They are essential when selling products with multiple options.
For example, a Type field might specify “Charger,” while a Material field lists “Plastic.” Dimensions such as height, width, and weight can be entered for logistics and shipping purposes.
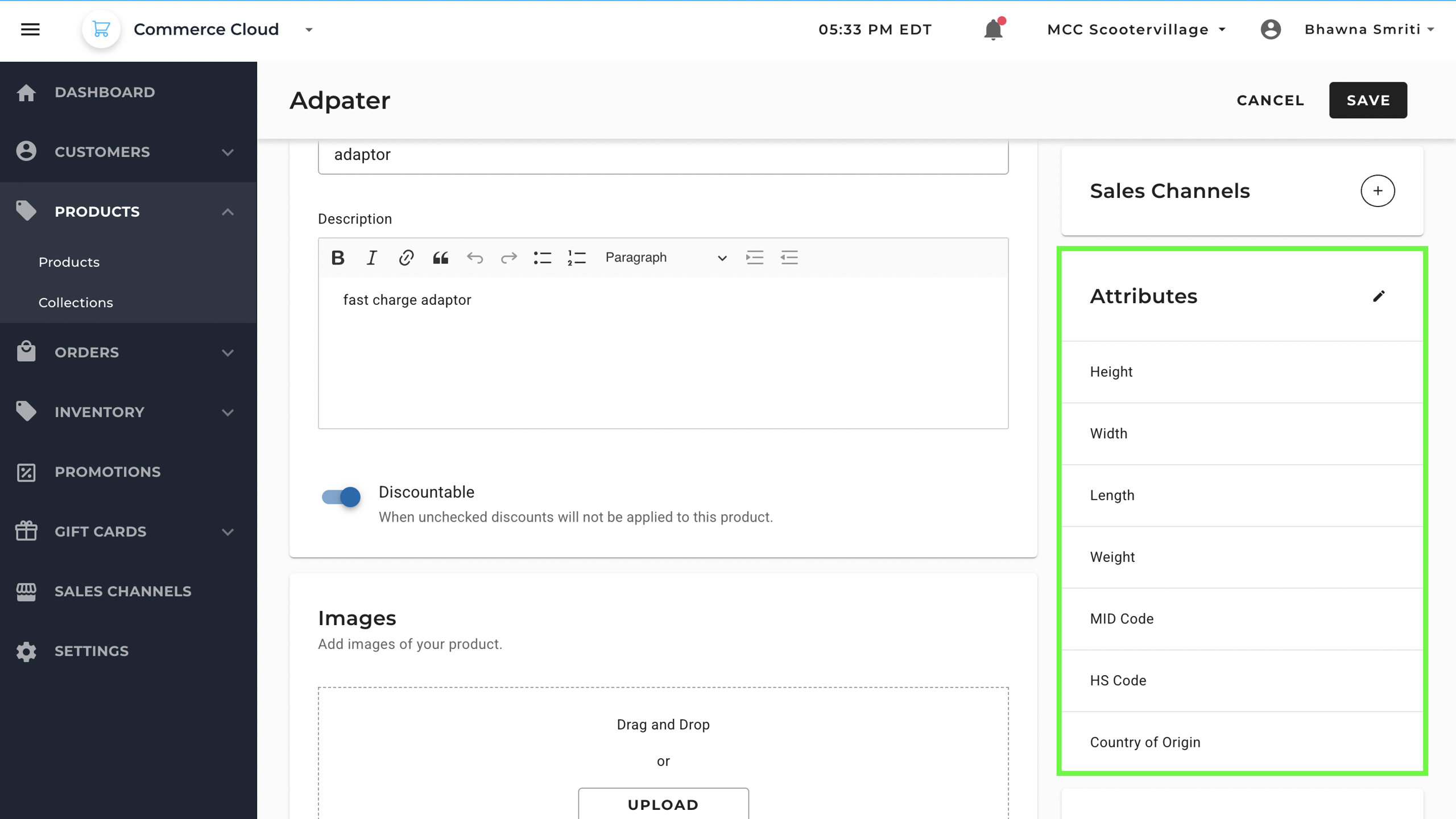
Shipping Attributes:
- Height, Width, Length, Weight – Physical dimensions for shipping and display.
- MID Code – Manufacturer Identification Code
- HS Code – Internationally standardized numerical code used to classify traded products.
- Country of Origin – Country where a product is manufactured/produced
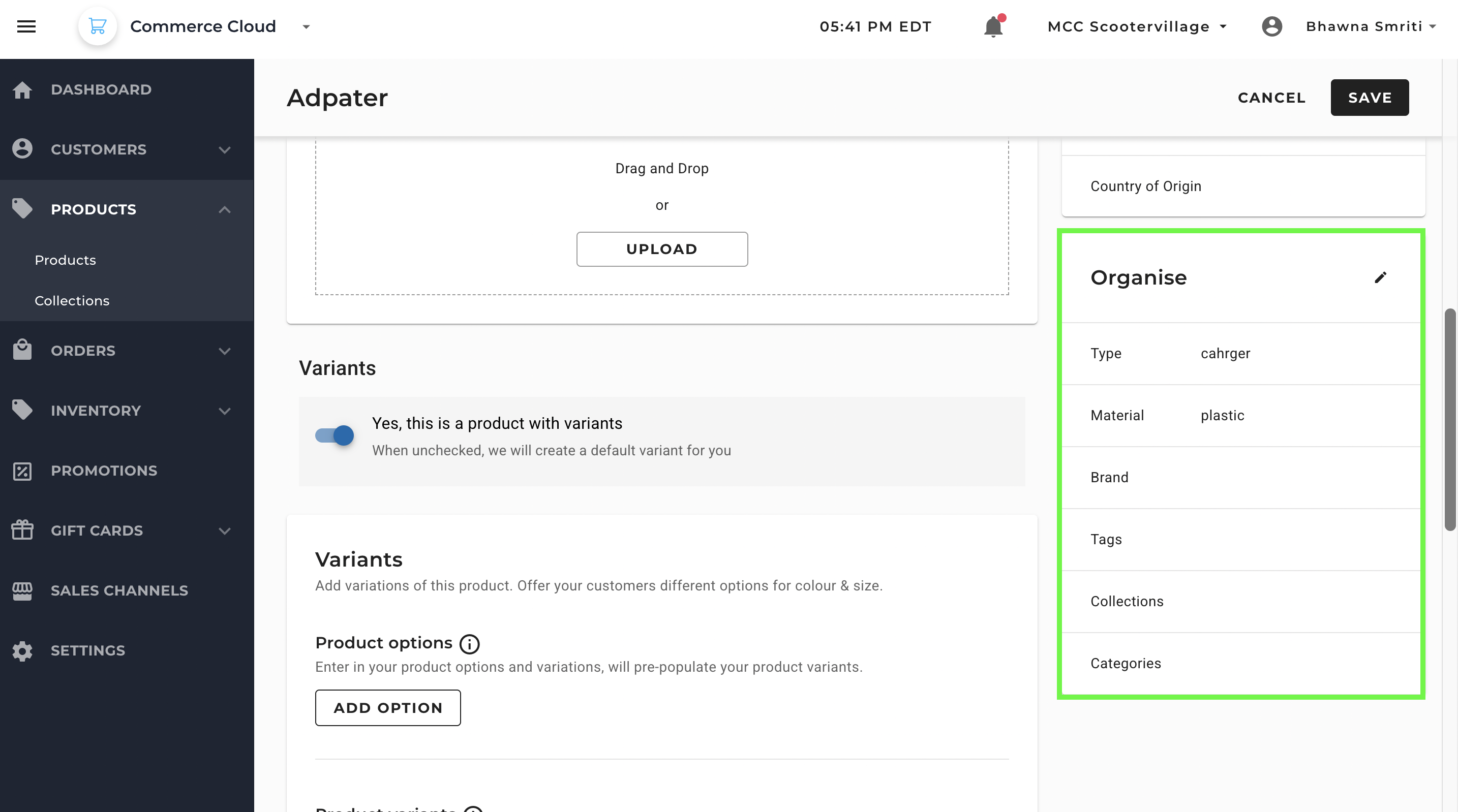
You can also assign brands, tags, and connect the product to categories under “Organise” for internal organization or to collections for storefront merchandising.
- Type - General category or nature of the product
- Material - Primary substance or composition of the product
- Brand - Name of the company or trademark under which the product is sold
- Tags – Keywords to support search and filtering.
- Collections – Customer-facing groups powered by rules or manual selection.
- Categories – Internal classification for catalog organization.
3. Inventory
The Inventory section controls stock tracking and purchasing logic for the product. If you enable inventory management, the system will track quantities and automatically adjust them when sales, returns, or manual updates happen.
Note: If variants are enabled, inventory can be managed individually per variant.
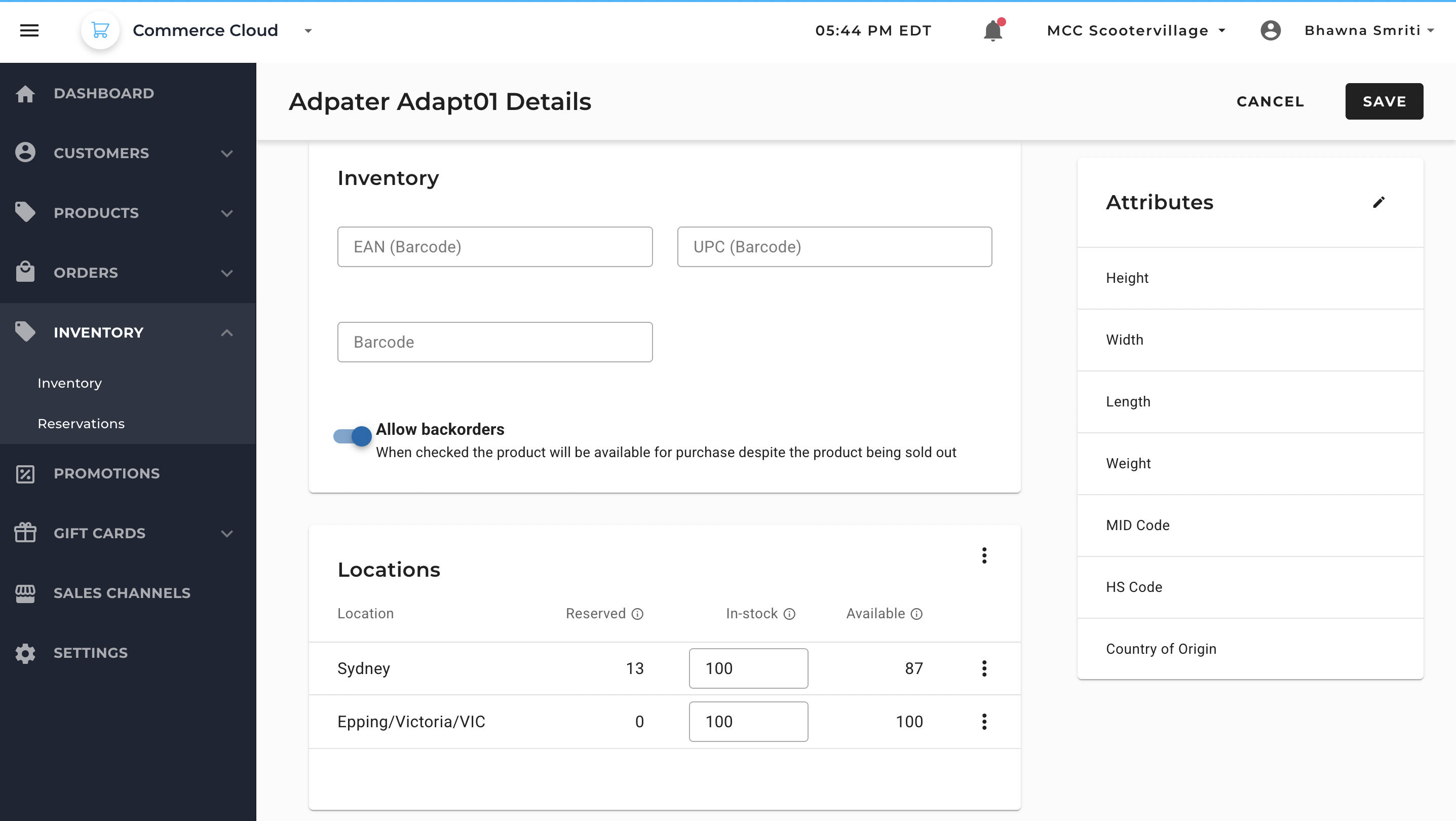
Inventory-related fields:
- EAN (Barcode) – European Article Number for scanning and tracking.
- UPC (Barcode) – Universal Product Code.
- Barcode – Alternate identifier for product scanning.
- Allow backorders toggle – Allows purchases even when stock is depleted.
- Stock table – Lists location-specific inventory quantities (e.g., Sydney – 100 units, Epping/Victoria/VIC – 100 units).
4. Pricing
You set the base price here, and if needed, you can use promotions tab to set pricing or discounts conditions. This is useful if you want to sell at a different price in a physical store versus online, or in different marketplaces.
MCC let you create discount campaigns for specific products, customer groups, or entire orders. These can be amount-based, percentage-based, or provide free shipping.
5. SEO Settings
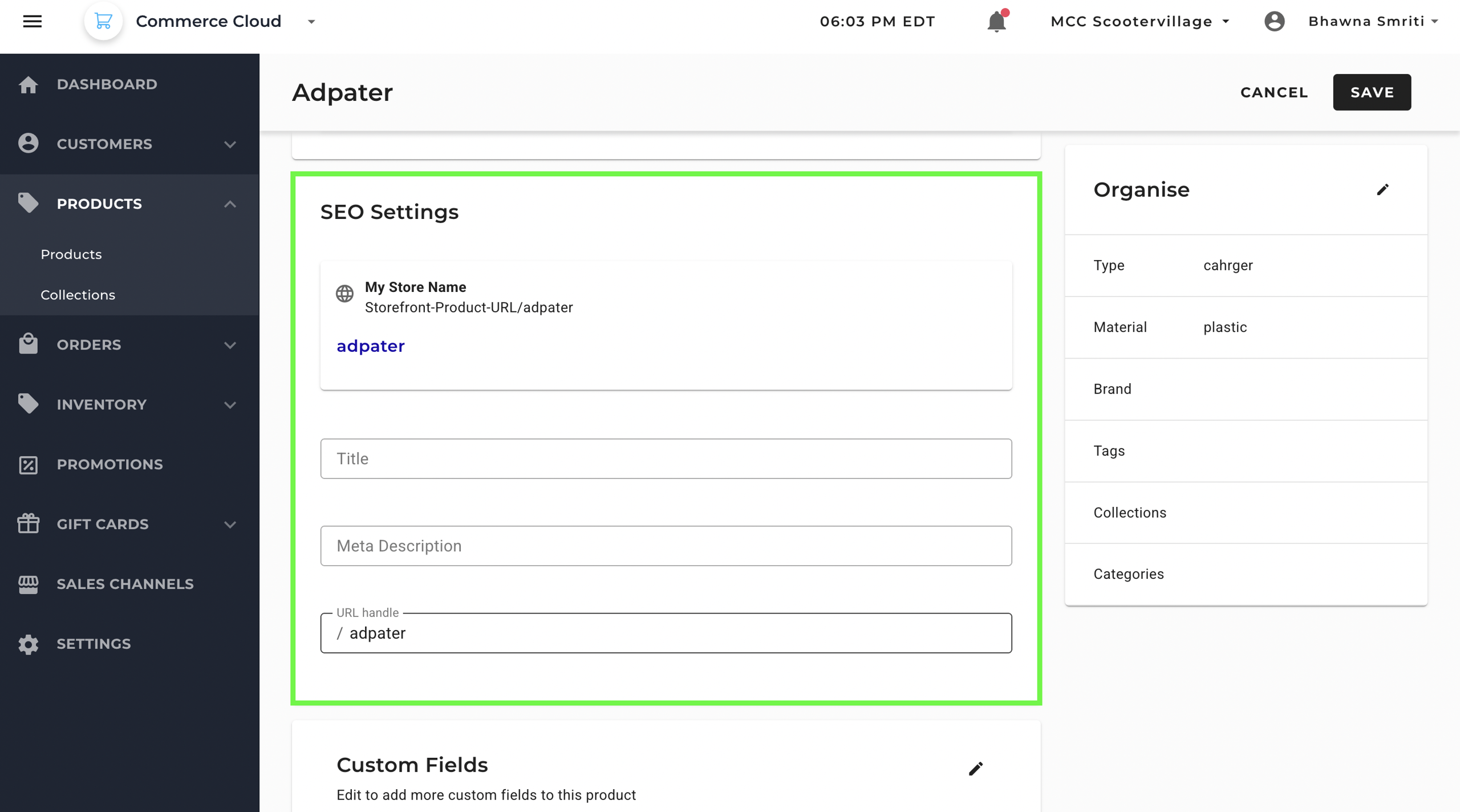
SEO settings determine how your product appears in search engine results and storefront URLs.
You can enter a meta title and description — both of which should include relevant keywords to improve discoverability — and customize the URL handle to make it short, readable, and SEO-friendly (e.g., /fast-charger instead of /product123).
Optimizing these fields helps search engines understand your product, making it more likely to appear for the right audience.
Fields include:
- Title – Meta title for SEO (can be different from storefront title).
- Meta Description – Search engine description snippet.
- URL Handle – Customizable part of the product URL (e.g.,
/adapter).
Tip: Use relevant keywords in the SEO title and description to improve product visibility in search results.
6. Custom Fields
6.1 Product Custom Field:
Custom Fields allow merchants to store additional, business-specific data beyond the standard Commerce Cloud fields. You can choose from several field types, such as short text, long text, date, number, decimal, or true/false.
Example fields from UI:
IsForSale – Boolean field indicating if the product is currently for sale.IsExpired – Boolean field marking whether the product listing has expired.SAT – Could be used for internal compliance or supplier reference codes.VAT – Can store applicable tax percentage or code.STORE – Indicates in which store the product is available.
In your setup, for example, you might use IsForSale or IsExpired to control product availability logic, or store tax codes like VAT and supplier identifiers like SAT.
Availability rules let you control which channels see these fields, and you can set them to active or inactive depending on whether they’re currently in use.
6.2 Custom Field Settings:
In addition to adding custom fields on a product record, Maropost Commerce Cloud lets you define global custom fields in Settings. These fields can then be applied consistently across multiple entities in your catalog and order flow.
Where Custom Fields Can Be Applied (Levels)
When creating a custom field, you choose the Level. This defines which type of entity the field attaches to:
Level | Description |
|---|
Product | Fields specific to the product itself (e.g., Warranty Info, Care Instructions). |
Variants | Fields tied to product variants (e.g., Batch Code, Size Guide). |
Collections | Fields applied to product groupings (e.g., Campaign ID, Seasonal Tag). |
Categories | Fields used on category structures (e.g., Display Banner, SEO Override). |
Orders | Fields that apply to order records (e.g., Gift Wrap, Delivery Preference). |
Supported Field Types
When adding a custom field, you also define its data type, which controls what kind of value can be stored:
Field Type | Purpose / Example |
|---|
Short Text | Small strings, like codes or short labels. Example: Model No. |
Text | Longer descriptive text. Example: Care instructions. |
Date | Date selector. Example: Expiry date, Launch date. |
Integer Number | Whole numbers only. Example: Warranty (years), Item count. |
Decimal Number | Numbers with decimals. Example: Alcohol % content, Weight (kg). |
True/False | Boolean values. Example: IsPreOrderAvailable (Yes/No), IsFragile (Yes/No). |
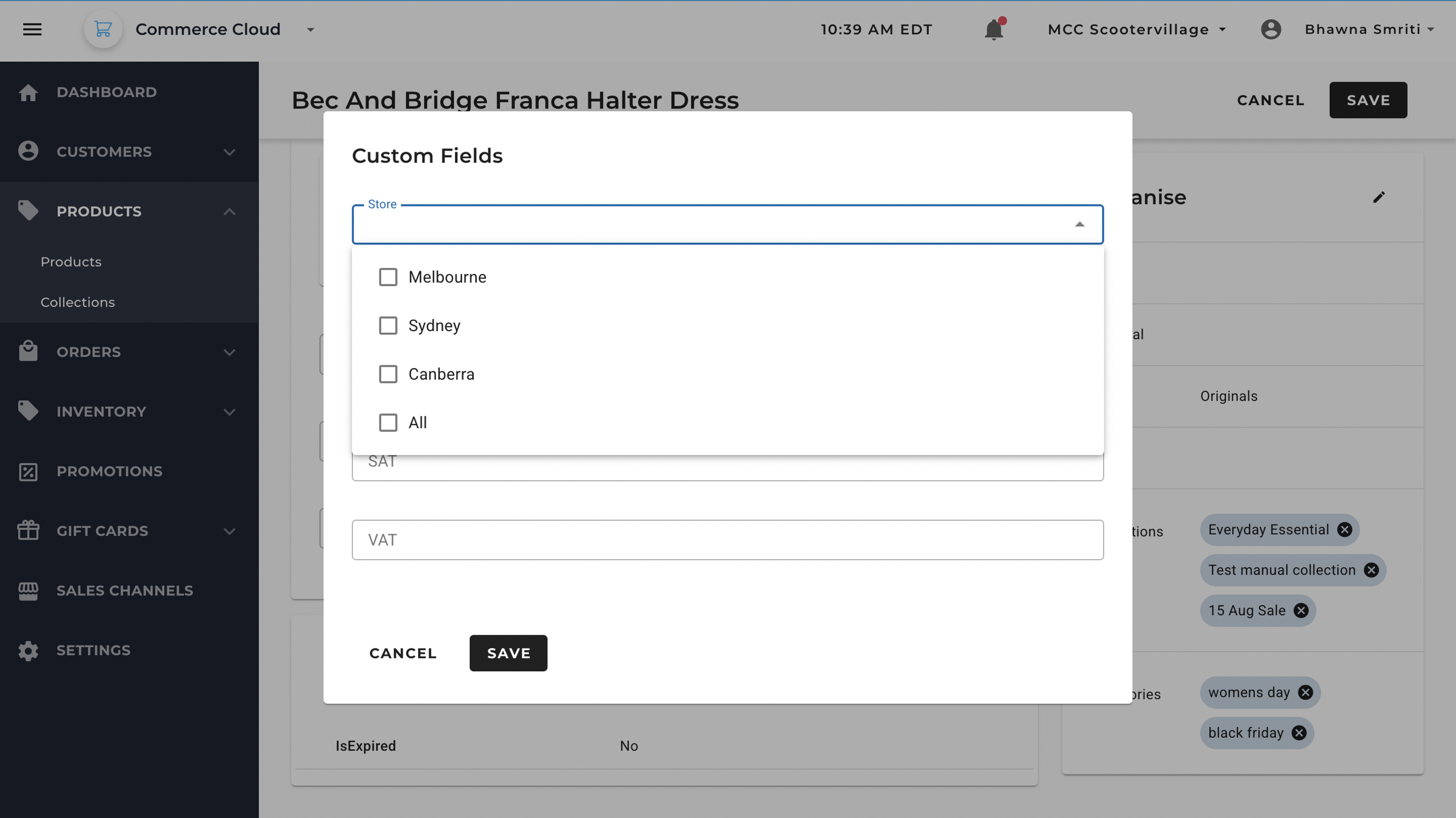
For example: If you want to create a custom field for the store availability of the product, you can create multi-select option to indicate its availability.
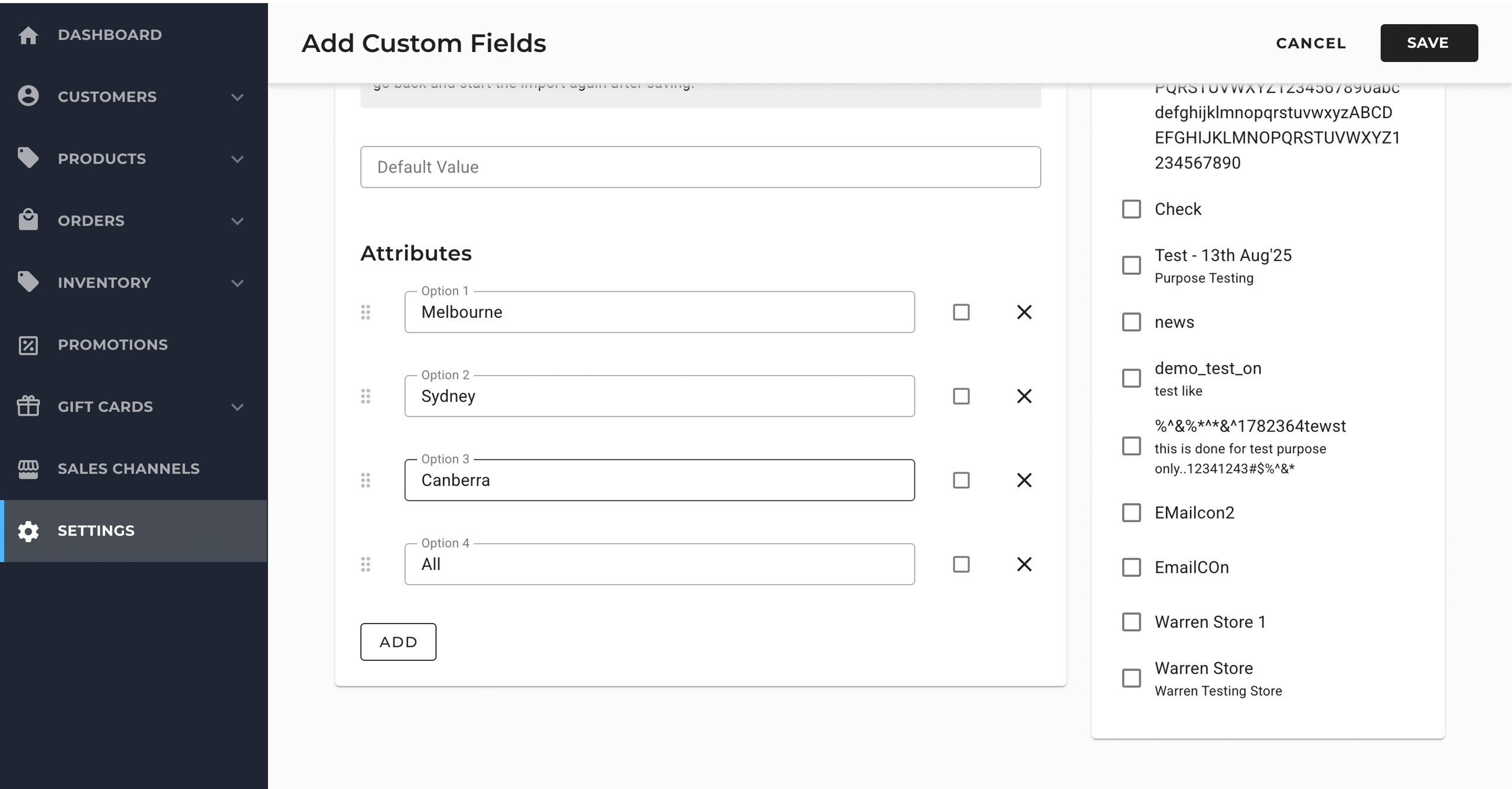
Once the setting is applied, you will be able to select the store availability option for new and existing products in the system.
How These Entities Work Together:
- General Information sets the product’s identity and where it’s sold.
- Attributes power variant creation and product classification.
- Inventory ensures accurate stock tracking and availability logic.
- Pricing determines the product’s sales price in each channel.
- SEO Settings improve discoverability in search engines.
- Custom Fields extend flexibility, allowing merchants to store and manage specialized data points.